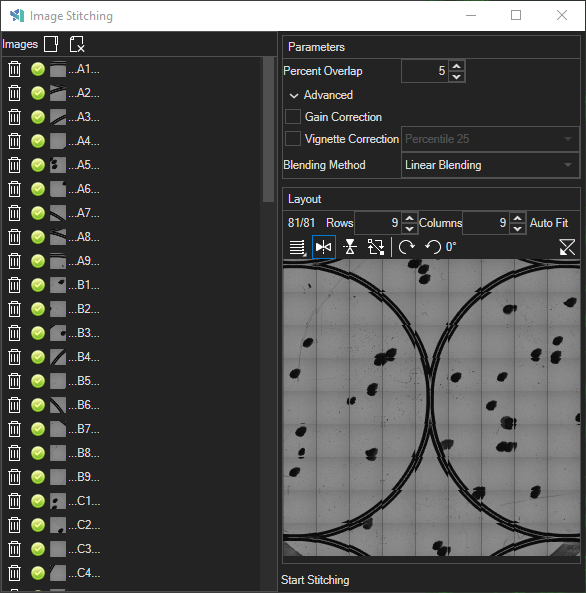
Parameters Panel
Here you specify the parameters for the stitching algorithm.
| Parameters Panel |
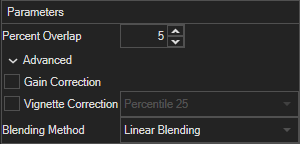
Percent Overlap
The percentage of the fovs that overlaps from the acquisition method.
Gain Correction
This option fixes the issue where the overall brightness/gain of each tile is slightly different, such as one corner of the stitched image may be brighter than the rest. This functionality first estimates the gain for each of the tiles and then corrects all tiles to create a stitched image with flatter illumination.
Vignette Correction
This option fixes the issue where individual tiles are slightly dimmer at the edges of each tile due the illumination at the center of the image. See a few examples of this issue: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vignetting
To correct vignetting, first the general background illumination for the microscope is determined by looking at all of the images as a whole/stack and measuring each pixel position across all tiles. Looking at each pixel across all tiles, the statistic you select is used to estimate the background that is effective at ignoring the tile specific content:
- Median: The median intensity value at each pixel location is considered the background.
- Percentile 25: The 25th intensity percentile value is considered the background.
- Min Value: The minimum value at each pixel location is considered the background.
- Max Value: The maximum value at each pixel location is considered the background.
Choosing the correct statistic for the background estimation depends on the image content, percentile 25 works well most of the time.
Once the background of the intensity image is estimated, the inverse of the background image is applied to each tile to flatten the intensity of the individual tiles.
Blending Method
The blending method determines what intensity value the algorithm should output when two or more tiles overlap. For most circumstances linear blending should be used.
- Linear Blending: The value of each pixel in the overlap region is a weighted sum where the pixels in the overlap region are inversely weighted by their distance to the center of each image. For example, if a pixel in an overlap area is closer to the center of image A, and further away from the center of image B, it will be weighted higher for image A since it is closer to the center of image A.
- Average Blending: The value of each pixel in the overlap is averaged over all images (that create the overlap) with equal weighting.
- Overlap Blending: No blending is performed and the pixels of the final stitching are set based upon column-row order of the tiles. A pixel in the final stitching is set by the last tile in a row to overlap that pixel.