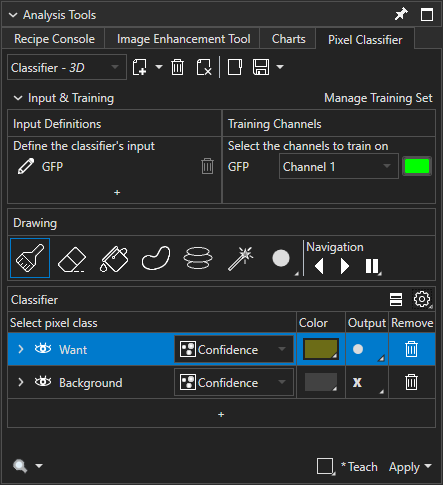
Classifier Toolbar
The Classifier Toolbar is located at the top of the Pixel Classifier tab. The toolbar lets you perform file actions related to the Pixel Classifier, such as creating a new classifier; saving a classifier, training set, or annotations; and loading classifier files.
Classifier Toolbar
The function for each item in the toolbar is summarized in the table below.
Function | Icon | Description |
|---|---|---|
Select Classifier | Shows the name and type (2D or 3D) of the currently selected classifier; click on the item to expand a dropdown menu from which you may select a loaded/created pixel classifier for training and/or applying | |
Create New | Allows you to create a new, blank pixel classifier for teaching; click on the downward-pointing triangle to expand a menu where you may specify whether to create a 2D or 3D classifier | |
Delete | Removes the current pixel classifier from Aivia; this does not delete the pixel classifier from its file if the classifier was loaded from a file | |
Remove All Classifiers | Removes all currently loaded classifiers | |
Load | Allows you to load a pre-trained pixel classifier (.pxclassifier), training set (.pxtraining), or set of annotations (.pxannotations) from a file | |
Save | Allows you to save the current pixel classifier, training set, or annotations to a file |
Drawing
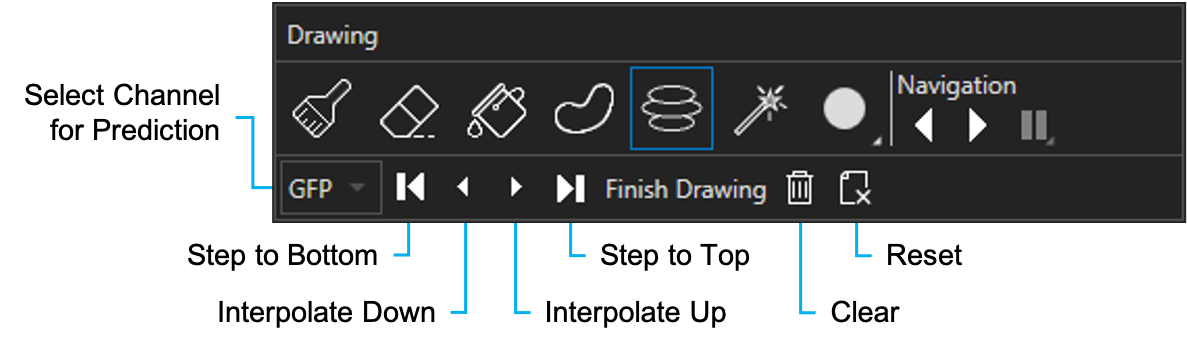
When teaching a pixel classifier, use the variety of drawing tools to draw some examples of your classes. All drawing, except with the Magic Wand, must be done in Main View (2D).
Drawing tools
The function and description for each of the drawing tools are summarized in the table below.
Function | Icon | Description |
|---|---|---|
Paint | Paints a circle under the cursor for the currently selected class; the brush size is adjustable | |
Erase | Erases a circle under the cursor for every class; the eraser size is adjustable | |
Flood | Fills in enclosed regions with the selected class; the enclosure can be made up of any class(es) | |
Region Drawing | Draws a freehand drawing that automatically closes | |
Auto Draw | Predicts the contour on the next z-plane based on previous drawing; see the "Auto Draw mode" section for more details | |
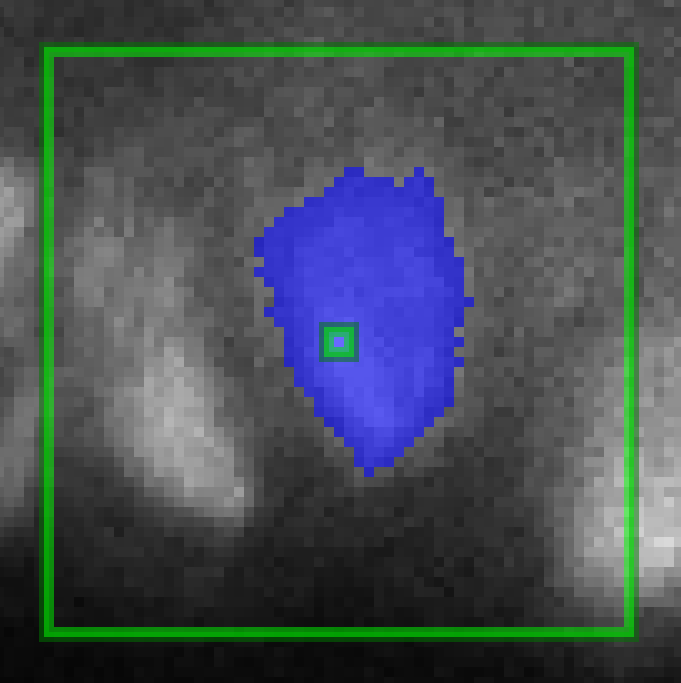
Magic Wand | Uses flood-filling to paint a region that has similar intensity and is connected to the selected location; in 3D, the Magic Wand paints regions for two (2) classes, one (1) for the selected class and one (1) for the background class or other class (see the "Magic Wand" section) | |
Size Selector | Adjusts the size of the brush or eraser | |
Jump to Previous Teaching Frame | Jumps to the previous frame with a teaching region drawn on it, moving back through Z and then through time | |
Jump to Next Teaching Frame | Jumps to the next frame with a teaching region drawn on it, moving forward through Z and then through time | |
Automatically Move to Next Frame (only available for 3D images) | Sets the mode for moving between z-frames after a drawing is completed; the modes are as follows:
|
Auto Draw mode
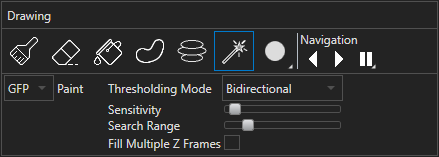
Auto Draw options
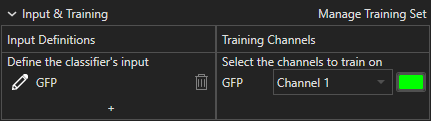
When Auto Draw mode is selected, a set of options are shown underneath the row of drawing tools (see above). First, select the channel to use for prediction in the dropdown menu on the left, which shows "GFP" in the example above. Click and drag the mouse to draw the outline of a region on the image; when the mouse button is released, the ends of the drawn line are automatically connected to create a closed loop. Use the Interpolate Down button and Interpolate Up button (or hotkeys S and D) to interpolate the next drawing down or up in Z respectively. The Step to Bottom button and Step to Top button (or hotkeys A and F) can be used to visit the bottom and top drawings respectively. Click on the Clear icon to remove all drawing from the current z-slice or on the Reset icon to clear all drawing. Click on Finish Drawing to assign the drawn regions (enclosed by the blue outlines) on all slices to the selected class.
Magic Wand
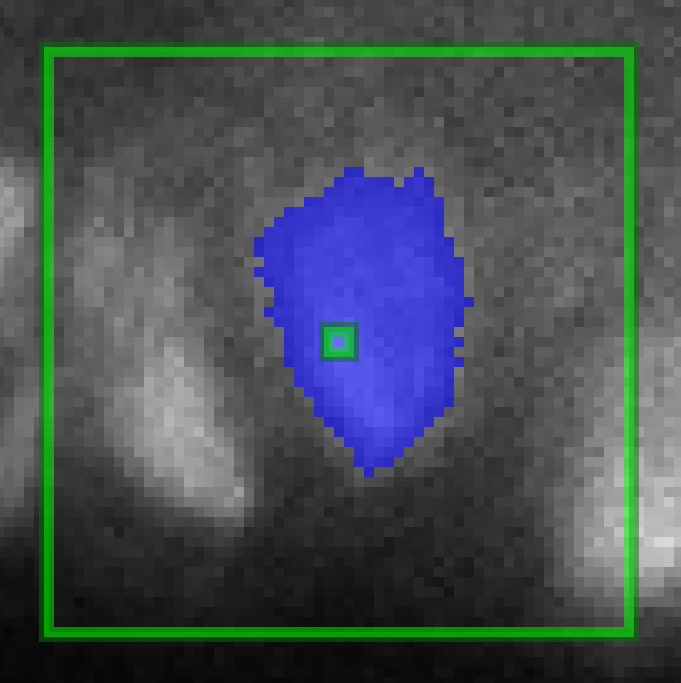
Magic Wand options
Options for the Magic Wand tool are provided below the row of drawing tools when the Magic Wand is selected (see above). The Magic Wand may be used for annotation in 2D or 3D viewing modes. In 2D or 3D, the first step is to select the image channel to use from the dropdown menu, which shows "GFP" in the image above.
In Main View (2D), expand the Thresholding Mode dropdown menu to choose one of the following modes:
Bidirectional mode accepts connected pixels within the sensitivity limit above and below the intensity at the selected location.
Peak Finding mode accepts connected pixels within the sensitivity limit above the intensity at the selected location.
Valley Finding mode accepts connected pixels within the sensitivity limit below the intensity at the selected location.
Hotkeys for drawing
Drawing mode | Hotkey | Description |
|---|---|---|
Paint |
| Switches to erasing while held down |
| Adjusts the brush size when done over the Image Panel | |
Erase |
| Switches to painting while held down |
| Adjusts the eraser size when done over the Image Panel | |
Auto Draw |
| Goes to the bottom drawing |
| Predicts the next drawing down | |
| Predicts the next drawing up | |
| Goes to the top drawing | |
| Clears all drawing | |
Magic Wand |
| Decreases the sensitivity |
| Increases the sensitivity | |
| Paints the selected region | |
| Adjusts the search range when done over the Image Panel |
Function | Icon | Description |
|---|---|---|
Expand/Collapse Output Parameters | Expands or collapses the output parameter section for each class | |
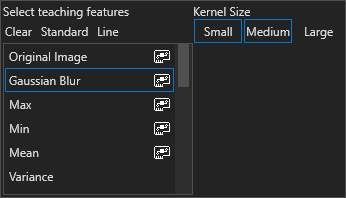
Advanced Options | Lets you select different features and kernel sizes to use for the pixel classifier | |
Hide/Show Class Annotations | Hides/Shows the training regions on the image | |
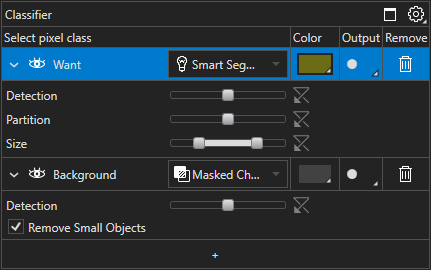
Select Output Type | Lets you select from the following four (4) output types for each pixel class:
| |
Class Color | Specifies the color of the drawn training region and, if Confidence is selected as the output, the channel color for the preview and output of the given class | |
Select Output | Opens the options for enabling/disabling output(s); you can disable the output for a given class by unchecking each available output; if Masked Channel is selected as the output, you may have the option to select multiple channels to mask out. | |
Remove Class | Removes the class from the pixel classifier | |
Add Class | Adds a new class to the pixel classifier |
Output parameters
Depending on the output type chosen, there are additional parameters that allow you to fine-tune the final output. To expand the parameters, click on the caret to the left of the Hide/Show Class Annotations button. The parameters are summarized in the table below by output type.
Output type | Parameter name | Description |
|---|---|---|
Masked Channel | Detection | Specifies the confidence threshold for the masked region; moving the slider to the right lowers the minimum confidence threshold and results in more pixels being included in the output |
Remove Small Objects | Removes small objects that are likely the result of noise | |
Segmentation | Detection | Specifies the confidence threshold for the segmented objects; moving the slider to the right lowers the minimum confidence threshold and results in detection of more low-confidence objects as well as larger and more connected objects |
Remove Small Objects | Removes small objects that are likely the result of noise | |
Smart Segmentation | Detection | Specifies the confidence threshold for the segmented objects; moving the slider to the right lowers the minimum confidence threshold and results in detection of more low-confidence objects as well as larger and more connected objects |
Partition | Specifies the aggressiveness of the partitioning algorithm applied to the segmented regions; moving the slider to the right increases the aggressiveness of partitioning and results in more partitioned objects | |
Object Size | Specifies the object size range based on the user-drawn regions; use the lower threshold (left slider control) to modify the minimum size and the upper threshold (right slider control) to modify the maximum size |
Apply Controls
The Apply Controls are located at the bottom of the Pixel Classifier tab and include options for previewing, teaching, and applying as well as specifying ROIs. Prior to applying a pixel classifier, the user must click the Teach button to train the pixel classifier.
Preview
Preview icon highlighted in the Apply Controls section
Click on the Preview icon (see above) to initiate preview generation; while previewing is toggled on, there is live previewing that updates as changes to the drawings/annotations are made. All output types may be previewed in Main View (2D), and Segmentation and Smart Segmentation outputs can be previewed in 3D View.
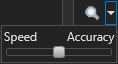
Click on the downward-pointing triangle next to the Preview icon to reveal the Speed/Accuracy slider (see below), which lets you control the quality of the preview. Moving the slider toward Speed leads to faster preview generation (at the expense of accuracy), while moving the slider toward Accuracy leads to the generation of previews that more closely resemble the output (but take longer to generate). If any ROIs are selected, previews are only generated in those ROIs.
Speed/Accuracy slider for previews
| Tip |
|---|
Turn previewing on while you are drawing to gauge when your annotations may be sufficient. |
General usage of the Pixel Classifier
Create a new pixel classifier
To create a new pixel classifier, click on the Create New icon in the Classifier Toolbar. A blank pixel classifier will then be created with two (2) pre-configured classes: "Want" and "Background." The general workflow for training a new pixel classifier is as follows:
1. Draw teaching regions using any tools in the Drawing section to paint desired features of interest. Select a different class from the class table to draw teaching regions for that class.
| Tip |
|---|
You need at least two (2) pixel classes, each with at least one (1) teaching region, to preview, train, and apply a pixel classifier. |
2. Preview the results. Use ROIs for faster previews.
3. Add more teaching regions to the image, following the same instructions as are in Step 1; keep previewing on to determine the quality of the teaching as you add more teaching regions.
| Tip |
|---|
You can load or switch to other images to add them to your training set. |
4. Teach the pixel classifier by pressing the Teach button.
5. Select the output types and destinations using the corresponding menus in each class's row of the class table.
6. Apply the pixel classifier to the image.
Save a pixel classifier
When you have a taught classifier that needs no further tuning, you may save the classifier as a .pxclassifier file; to do so, click on the downward-pointing triangle next to the Save icon in the Classifier Toolbar, select Save Classifier, choose the name and location for the file, and then click on Save. You may then load the classifier by clicking on the Load icon in the Classifier Toolbar, navigating to the .pxclassifier file, and then clicking on Open or by dragging and dropping the .pxclassifier onto the Pixel Classifier interface.
| Tip |
|---|
If you would like to save a taught classifier but there is a possibility you may want to change its settings or teaching regions later, save the training set instead of (or in addition to) the classifier. The training set file includes the taught classifier, if one is available, so that the classifier can be immediately applied in the future but can also be retaught. |
Technical details
The Pixel Classifier consists of two (2) fundamental steps:
Feature Calculation: Image features (such as edges) are calculated for every pixel of the input image to generate a feature vector.
Classification Application: The feature vector is used to train a classifier to classify unknown feature vectors into one (1) of the classes specified by the user.
Each image feature is derived from applying one (1) of several processing filters on the image over several scales, or kernel sizes, to identify both regional (macro) and local (micro) features inherent in the image. A random forest algorithm is used for creating the pixel classifier from the calculated features.
The classification result is output as new image channels that map the probability that a given pixel belongs to a specific class from 0 (high likelihood of not belonging) to 255 (high likelihood of belonging). The probability map channel can then be used for additional analysis.
Related articles
| Filter by label (Content by label) | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Page Properties | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
|